Entries in category: 4
Shown entries: 1-4 |
|
Sort by:
Date ·
Name ·
Comments ·
Views
S. Pogodin, V.A. Baulin, Soft Matter, 2010, 6, 2216 - 2226 
The Single Chain Mean Field theory is used to simulate the equilibrium structure of phospholipid membranes at the molecular level. Three levels of coarse-graining of DMPC phospholipid surfactants are present: ...
|
S. Pogodin, V.A. Baulin, ACS Nano, 2010, 4 (9), pp 5293–5300 
Great efficiency to penetrate into living cells is attributed to carbon nanotubes due to a number of direct and indirect observations of carbon nanotubes inside the cells. ...
|
V.A. Baulin, A. Johner, and J. Bonet Avalos, J. Chem. Phys. 133, 174905 (2010) 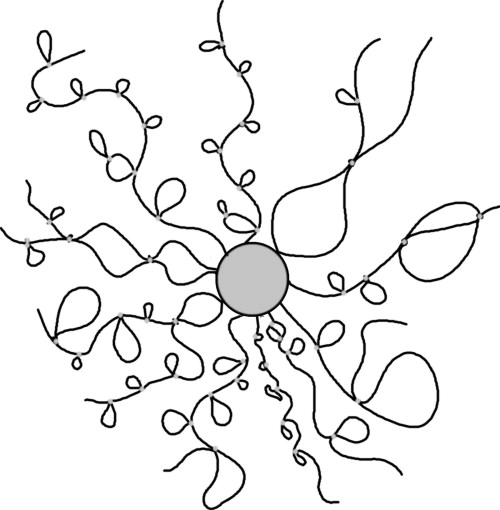
The interaction of amphiphilic polymers with small colloids, capable to reversibly stick onto the chains, is studied. Adhesive small colloids in solution are able to dynamically bind two polymer segments. This association leads to topological changes in the polymer network configurations, such as looping and cross-linking, although the reversible adhesion permits the colloid to slide along the chain backbone. Previous analyses only consider static topologies in the chain network. We show that the sliding degree of freedom ensures the dominance of small loops, over other structures, giving rise to a new perspective in the analysis of the problem...
|
S. Pogodin, N.K.H. Slater, V.A. Baulin, ACS Nano, 2011, 5 (2), pp 1141–1146 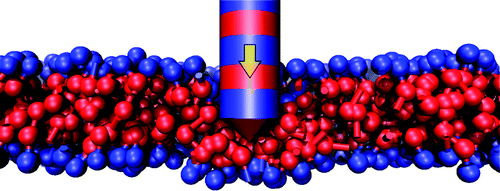
Nanotube patterning may occur naturally upon the spontaneous self-assembly of biomolecules onto the surface of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs). It results in periodically alternating bands of surface properties, ranging from relatively hydrophilic to hydrophobic, along the axis of the nanotube. Single-chain mean field (SCMF) theory has been used to estimate the free energy ...
|
|
|
|
