We explore the capabilities of the
Single Chain Mean Field Theory (SCMFT) developed at the URV in direct applications to the design and conception of drug carriers. The method is very competitive when compared to Monte Carlo simulations and is therefore suited for an exhaustive exploration of the compositions and molecular structures, such as those required to properly tune the properties of drug carriers. This computational method best suits the purposes of this area, since it can describe such nanoscale objects including details at the molecular level. In addition, we hope to fill with this comprehensive method the huge lack of even qualitative modeling in the domain of drug carriers.
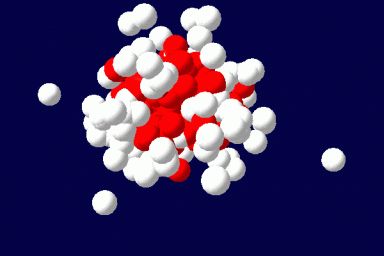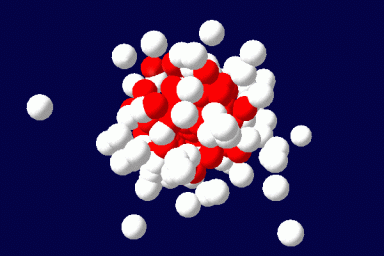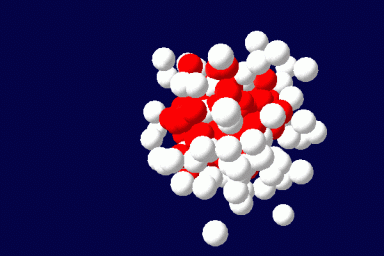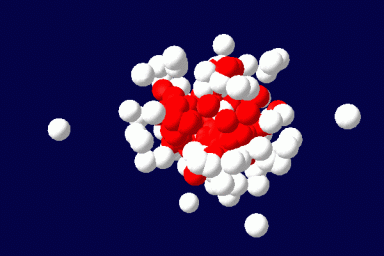
The method exactly accounts for the configurations of a single microscopically detailed chain at the molecular level. The interactions between different chains are described self-consistently through a mean molecular field. This mean field is found self-consistently. This method can be applied to solutions of linear or branched polymers, solutions of low-molecular weight surfactants and various additives, and mixtures of various components. It can be extended for the description of ordered phases, like liquid crystals, and to disordered structures as gels. The methodology of the SCMFT by its construction can be especially successful when used in parallel for the description of nano-objects like polymeric drug carriers.(Read more)
